Pocket Flow transforms codebases into easy-to-understand tutorials through AI.#
#AI #Codebase #Tools
GitHub - The-Pocket/PocketFlow-Tutorial-Codebase-Knowledge: Pocket Flow: Codebase to Tutorial
VoltAgent#
VoltAgent, an open-source TypeScript AI agent framework, simplifies the development of AI agent applications. It provides a range of modular building blocks and tools to help developers quickly build various AI applications, from simple chatbots to complex multi-agent systems.
#AI #Tools #Agents
From Mainframe Era to AI Agents: The Long Journey to Truly Personal Tech#
Sean Falconer explores the evolution of technology from the mainframe era to the age of AI agents, and the development of personal technology experiences throughout this process. While each wave of technological change in the past promised a more personalized experience, it wasn't until the advent of AI that technology truly began to adapt to users rather than forcing users to adapt to technology.
During the mainframe era from the 1950s to the 1970s, computers were massive shared machines, and users had to adapt to the machine's rules by inputting commands through terminals, with no personalization. In the desktop computer era of the 1980s to 1990s, the emergence of graphical user interfaces (GUIs) allowed users to interact by clicking icons and menus, but software still could not learn and adapt based on user behavior; users still had to learn how to use the software. Subsequently, the proliferation of the internet allowed users to choose browsers, browse websites, and search for information, but interactions remained insufficiently personalized, with recommendation systems based only on general trends and broad categories. Entering the mobile era of the 2000s, smartphones enabled users to access personalized information anytime and anywhere through apps and touchscreen technology, but this personalization was still rule-based rather than true intelligent learning.
The emergence of AI changed this landscape. AI can not only provide personalized content based on user behavior and preferences but also enable users to interact with technology in the most natural way through natural language processing technologies. AI systems can learn users' intentions and behavior patterns, allowing them to adjust and optimize user experiences in real-time. For example, Spotify and Netflix use AI to analyze user behavior data to provide personalized music and film content recommendations, significantly enhancing user engagement and satisfaction. In the e-commerce sector, Amazon achieved up to a 35% revenue increase through AI-driven product recommendation systems. Sephora combines AI and augmented reality (AR) technologies to provide users with personalized beauty advice, increasing user engagement and conversion rates. Nike's "Nike By You" platform offers users a customized product design experience through AI.
The rapid development of AI technology is supported by technologies such as large language models (LLMs), retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), and adaptive systems. LLMs can understand and generate natural language, allowing users to interact with systems in a natural way. RAG technology allows models to retrieve real-time information before generating responses, ensuring the accuracy and timeliness of output content. Adaptive systems continuously optimize their performance and recommendation effectiveness by monitoring user behavior and feedback.
As AI technology continues to evolve, future applications will no longer just be tools for users but partners that can grow and evolve alongside them. These applications will adjust and optimize user experiences in real-time by learning user behaviors and preferences, providing more natural and useful interaction methods. However, as the level of personalization in technology increases, ensuring fairness, transparency, and accessibility becomes crucial to ensure that all users can benefit.
#AI #Thoughts #UserExperience
From Mainframes to AI Agents: The Long Journey to Truly Personal Tech
OpenDeepWiki Source Code Interpretation#
#AI
OpenDeepWiki Source Code Interpretation
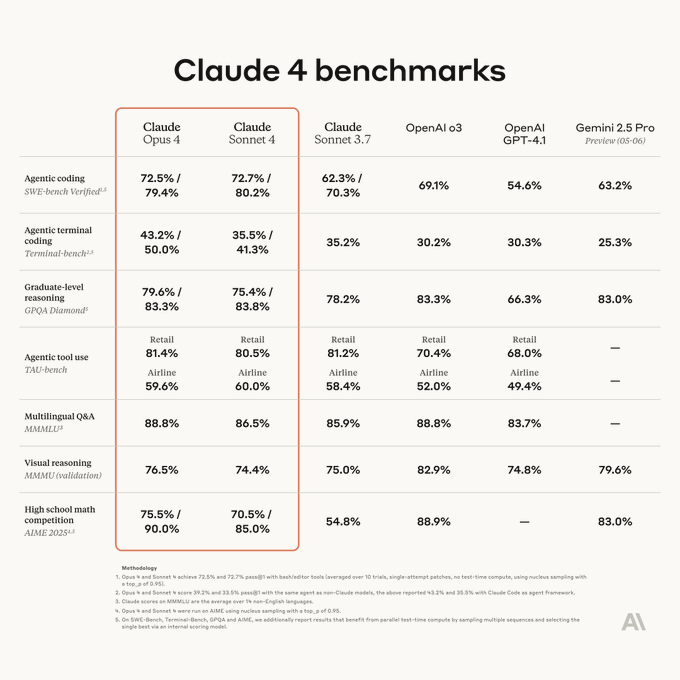
Claude 4 Released#
Claude 4 is the next-generation AI model launched by Anthropic, including Claude Opus 4 and Claude Sonnet 4. Here are its main features summarized:
- Advanced programming capabilities: Claude Opus 4 is currently the strongest programming model, performing excellently in benchmark tests like SWE-bench, capable of handling complex coding tasks for extended periods, with error rates reduced from 20% to nearly 0. It supports code generation and debugging in over 20 programming languages, suitable for managing complex codebases.
- Hybrid reasoning modes: It offers both instant response and extended thinking modes, with the latter supporting in-depth reasoning and tool usage (such as web searches), enhancing the quality of responses for complex tasks.
- Enhanced multimodal capabilities: It supports text and image processing and may expand to video content analysis and image generation, suitable for applications in media, education, and security.
- Expanded context window: It maintains a context window of 200K tokens (about 350 pages of text), suitable for handling long documents and complex dialogues, with better context retention than previous generations.
- Advanced reasoning and problem-solving: It excels in graduate-level reasoning (GPQA), mathematics, and logic tasks, with reasoning capabilities improved by 40% over Claude 3.5 and a 60% reduction in math error rates.
- Ethics and safety: It continues Anthropic's constitutional AI approach, strengthening safety measures and bias mitigation to ensure responsible AI behavior in compliance with global regulations like GDPR.
- Efficient performance and cost: Processing speed increased by 2.5 times, maintaining high performance while being cost-effective, priced at Opus 4 ($15/million input tokens, $75/million output tokens) and Sonnet 4 ($3/million input tokens, $15/million output tokens).
- Enterprise-level applications: It provides SDKs, real-time debugging, and open-source plugins, supporting cross-platform integration for complex workflows in industries like retail, healthcare, and education, such as data analysis, personalized experiences, and automation tasks.
- Multilingual support and globalization: It supports real-time translation and content generation in multiple languages, enhancing global accessibility.
- User experience optimization: It offers a "styles" feature to customize writing styles, supports content creation and technical documentation; the "artifacts" feature generates interactive content; and supports memory optimization for long-term tasks, enhancing continuity.
Limitations: Visual recognition capabilities may not match Gemini 2.5, requiring more precise prompt engineering to fully leverage performance.
Claude 4 significantly enhances programming, reasoning, and multimodal capabilities, emphasizing ethical AI and enterprise applications, suitable for scenarios requiring deep reasoning and complex task handling.
#Claude #AI
Anthropic Releases Claude Opus 4 and Claude Sonnet 4.#
Claude Opus 4 is the most powerful model to date and the best coding model in the world.
Claude Sonnet 4 has significant upgrades over its predecessor, offering exceptional coding and reasoning capabilities.
#Claude #AI
Ignite Creativity with New Generative Media Models and Tools#
The Google DeepMind team has released a series of new generative media models and tools designed to inspire creativity and provide creators with more means of expression. These models include Veo 3, Imagen 4, and Flow, which have made significant breakthroughs in image, video, and music generation, helping artists turn their creative visions into reality.
Veo 3 is Google's latest video generation model, surpassing Veo 2 in quality and achieving synchronized video and audio generation for the first time, such as generating background traffic noise in urban street scenes or bird songs in parks, and even generating dialogues between characters. Veo 3 excels in text and image prompts, realistic physical effects, and precise lip-syncing, capable of generating corresponding video clips based on user story descriptions. Veo 3 has been launched in the U.S. for Ultra subscribers of the Gemini application and Flow users, while enterprise users can access the model on Vertex AI.
Imagen 4 is Google's latest image generation model, combining speed and accuracy to generate images with astonishing detail clarity, accurately presenting complex fabric textures, water droplets, and animal fur. The model supports various aspect ratios and image generation up to 2K resolution, suitable for printing or presentations. Additionally, Imagen 4 has made significant improvements in spelling and typography, making it easier to create greeting cards, posters, and even comics. Imagen 4 has been launched in the Gemini application, Whisk, Vertex AI, and Workspace tools such as slides, videos, and documents, with a faster variant set to be released soon, generating images 10 times faster than Imagen 3, allowing for quicker exploration of creativity.
Flow is an AI film production tool designed for Veo, integrating Google's DeepMind's state-of-the-art models, including Veo, Imagen, and Gemini. Users can describe shots in natural language, manage characters, scenes, items, and styles in their stories, weaving these elements into beautiful scenes. Flow has been launched in the U.S. for Google AI Pro and Ultra plan subscribers, with plans to expand to more countries in the coming months.
Additionally, Google announced updates to Lyria 2, a music generation model that provides experimental tools for musicians, producers, and songwriters to inspire new creative ideas. Lyria 2 is now available to creators and enterprise users through YouTube Shorts and Vertex AI. Google also launched Lyria RealTime, an interactive music generation model capable of generating, controlling, and performing generative music in real-time, which users can access through API or AI Studio.
In terms of responsible creation, Google has marked over 10 billion images, videos, audio files, and texts with SynthID watermark technology since 2023 to help identify AI-generated content and reduce the likelihood of misinformation and misattribution. Content generated by Veo 3, Imagen 4, and Lyria 2 will continue to carry SynthID watermarks. Additionally, Google has launched SynthID Detector, a verification portal where users can upload content to check for SynthID watermarks, determining whether the content was generated by AI.
#Google #AI #Tools
Fuel your creativity with new generative media models and tools
Claude Code SDK#
The Anthropic team has launched the Claude Code SDK to help developers integrate Claude Code functionality into applications. This SDK currently supports command-line use, with TypeScript and Python versions to be released in the future.
In basic usage, developers can run Claude Code in non-interactive mode via the command line, for example, by directly passing prompts using the -p parameter or piping input to Claude Code. Additionally, output formats can be specified as text, JSON, or streaming JSON to meet different development needs.
In advanced usage scenarios, the SDK supports multi-turn dialogue functionality, allowing developers to continue recent conversations or restore specific dialogues via session IDs. Furthermore, custom system prompts can guide Claude's behavior, such as specifying it to respond in a specific role (e.g., senior backend engineer or database architect). The Model Context Protocol (MCP) configuration allows developers to extend Claude Code's capabilities by loading tools and resources provided by external servers, such as file system access or GitHub integration.
In terms of CLI options, the SDK offers a rich set of command-line options, including non-interactive mode execution, specifying output formats, restoring sessions, limiting dialogue turns, and overriding or appending system prompts. These options provide developers with flexible control capabilities to adapt to different development scenarios.
Output formats support various types. The default text output returns only the response text; JSON output includes structured data and metadata, such as cost, duration, and session ID; streaming JSON output returns messages one by one, suitable for handling multi-turn dialogues.
In terms of message architecture, the returned messages strictly follow a specific pattern, including assistant messages, user messages, session initialization messages, and final result messages. Each message type contains specific fields, such as session ID, message type, and subtype.
Best practices recommend that developers use JSON output format for easier program parsing and gracefully handle errors by checking exit codes and error logs. Additionally, it is advised to utilize session management features to maintain context in multi-turn dialogues and set timeouts and adhere to rate limits when necessary.
In practical application scenarios, the Claude Code SDK can be deeply integrated into development workflows, such as providing automated code reviews, creating pull requests, and issue classification through GitHub Actions. The Anthropic team also provides comprehensive CLI documentation, tutorials, and related resources to help developers better utilize the SDK.
#Claude #AI #SDK
How to Ensure a Good User Experience While Improving Product Conversion Rates?#
User onboarding design aims to help users quickly get started with products and lower the barrier to use, but in the pursuit of conversion rates, it can sometimes turn into a form of "gentle control," potentially infringing on users' basic rights. For instance, some products write the terms "automatically renew after a 3-day trial" in very small print when guiding users to activate memberships, while the process for canceling subscriptions is extremely complicated. Although this design may improve conversion rates in the short term, it can damage users' trust in the long run and even pose risks of violating laws and regulations.
To achieve a balance between user experience and conversion rates, DesignLink offers the following suggestions:
- Respect users' right to choose: Designs should genuinely empower users with the right to choose, rather than forcing decisions through visual or interactive means. For example, the "agree" button should not be overly prominent while the "decline" option is hidden or downplayed. Clear exit paths should also be provided, allowing users to easily cancel actions or decide later.
- Ensure transparency of user information: When requesting user permissions or collecting user data, it is essential to clearly inform users of the purpose, content, and consequences. For instance, when access to users' microphones or cameras is needed, the purpose should be clearly stated instead of confusing users with vague phrases like "for a better service experience." Additionally, important information such as user agreements should be presented in plain language, avoiding overly complex legal jargon.
- Empower users with data control: Users should be able to easily manage their data, including exporting, modifying, and deleting it. Product designs should provide convenient data management features, allowing users to view and control their data at any time.
- Optimize exit and cancellation processes: The process for canceling subscriptions or exiting services should be straightforward, avoiding excessive obstacles. For example, users should not be required to fill out complex questionnaires or contact customer service when canceling subscriptions; instead, a one-click cancellation feature should be provided. Additionally, after cancellation, users should retain access to their data for a period, allowing them to restore services at any time.
Design ethics are crucial in user experience design. Designers should be user-centered, thinking from the users' perspective to ensure that users feel safe, free, and respected while using products. For instance, during the design of key nodes such as registration, payment, or sharing, clear and understandable options should be provided, along with a secondary confirmation mechanism to prevent users from regretting due to misoperation.
DesignLink proposes methods to establish a sustainable experience and rights balance model. For example, adopting a "three-stage design review mechanism" to confirm whether users genuinely need a feature before it goes live, checking mid-term whether users can independently control the onboarding process, and collecting user feedback in the later stages to continuously optimize the product. Additionally, the design model should possess fairness, explainability, reversibility, and feedback mechanisms to ensure that all users can smoothly use the product and can change their minds or provide feedback at any time.
#UserExperience #ExperienceDesign
How to Ensure a Good User Experience While Improving Product Conversion Rates?
Google Stitch#
Google has released Stitch, touted as the simplest and fastest product for generating outstanding designs and UI interfaces.
Stitch is an AI-driven tool that helps app builders generate high-quality user interfaces for mobile and web applications and easily export them to Figma or directly access front-end code.
#Google #AI
Google Announced a Series of New AI Models, Tools, and Subscription Services at I/O 2025#
Generative Media
- Veo 3 is Google's most advanced video generation model, capable of creating videos with sound effects and even dialogues. Currently, in the U.S., Google AI Ultra subscribers can use it through the Gemini app and Flow, and it can also be privately previewed on Vertex AI, with a broader rollout planned in the coming weeks.
- Veo 2 is gaining new features, such as reference-driven videos (for consistent styles and characters), camera controls for precise shot adjustments, external painting for extended aspect ratios, and object addition/removal. Some new controls are now available in Flow, with a full set of controls coming soon to Vertex AI.
- Imagen 4 can generate richer, more detailed, and accurate images, improving text rendering and quick results, now available for free in the Gemini app, Whisk, Workspace (slides, documents, videos), and Vertex AI, with a new fast version set to launch soon.
- Flow is a brand-new AI filmmaking tool that allows you to create movie clips using Veo, Imagen, and Gemini through natural language and asset management; it is now available for Google AI Pro and Ultra subscribers in the U.S.
- Google's music generation model Lyria 2 is now live on Vertex AI for high-fidelity adaptive music generation, while Lyria RealTime can be used as an experimental interactive music model through the Gemini API and Google AI Studio for real-time creation and performance of generative music.
Gemini Applications
- Canvas has added a one-click "Create" button, allowing users to easily convert chat content into interactive content, such as infographics, quizzes, and podcasts in 45 languages, while Deep Research now allows users to upload files and images, with Google Drive and Gmail integration coming soon.
- Gemini Live camera and screen sharing features are now available for free on Android and iOS (rolling out), and will soon integrate with Google apps like Calendar, Keep, Maps, and Tasks.
Subscriptions
- Google AI Pro ($19.99/month) is available in the U.S. and other countries, but some of the latest features (like Flow or Gemini in Chrome) will launch first in the U.S. with plans for broader rollout.
- Google AI Ultra ($249.99/month, with a 50% discount for new users for the first three months) offers the highest usage limits, earliest access to advanced models like Veo 3 and Gemini 2.5 Pro Deep Think, highest limits for Flow, and exclusive use of Agent Mode, along with YouTube Premium and 30TB of storage, now available in the U.S. with more countries coming soon.
- University students in the U.S., U.K., Brazil, Indonesia, and Japan can get a free year of Google AI Pro.
Gemini in Chrome and Agent Mode
- Gemini in Chrome is rolling out on desktop for Google AI Pro and Ultra users in the U.S. (English), allowing you to summarize, clarify, and get help with any webpage you are reading, with privacy controls ensuring Gemini only acts when you request it.
- Agent Mode will soon be available for Ultra desktop users, allowing Gemini to use the MCP protocol and automatically navigate online to handle complex goals, such as filtering lists, filling out forms, or arranging based on search results.
AI Applications in Search
- The AI mode will be rolled out to all U.S. users in the form of a new tab in Google Search, powered by Gemini 2.5, offering advanced reasoning, longer queries, multimodal search, and instant high-quality answers, with "deep search" capable of conducting hundreds of searches simultaneously and synthesizing cited reports.
- Real-time features of Project Astra (pointing your camera at what you see), Project Mariner's agent tools (buying tickets, making reservations, managing tasks), and personal context from Gmail or other Google apps will enter AI mode, controlled by users.
Gemini 2.5
- Gemini 2.5 Pro and 2.5 Flash are leading coding and reasoning benchmarks, with Gemini 2.5 Flash having a new preview version that offers better speed, efficiency, and coding/reasoning capabilities, both models set to be fully launched in June 2025.
- Gemini 2.5 Pro Deep Think introduces an experimental enhanced reasoning mode, including parallel thinking techniques for complex tasks, initially launching through the Gemini API to trusted testers before allowing users to control the depth and speed of answers.
- Gemini API and SDK natively support the Model Context Protocol (MCP), making it easier to integrate agents and tools across systems.
- Gemini API and Vertex AI now offer "thought summaries," explaining Gemini's reasoning and tool usage step-by-step.
Project Starline -> Google Beam, Astra -> Gemini Live, Mariner -> Agent Mode
- The Starline project has been renamed Google Beam, an AI-driven 3D video calling platform that transforms 2D streaming into immersive, lifelike meetings, set to launch later this year in collaboration with HP and other corporate partners.
- Gemini Live incorporates Astra's real-time camera and screen sharing features, which are now available for free on Android and have been launched on iOS.
- Project Mariner's agent computing features (such as multitasking and browser automation) are now available to U.S. Ultra users and will soon be opened to developers through the Gemini API and Vertex AI.
Open Models and Development Tools
Gemma 3n is a new efficient multimodal open model designed for fast, low-memory devices, supporting text, audio, images, and multilingual input, currently available for developer preview on AI Studio and AI Edge.
- Jules is an asynchronous coding agent powered by Gemini 2.5 Pro, currently in public testing and free, capable of handling real coding tasks in GitHub or your repo, with concurrent tasks and audio update logs.
- Gemini Diffusion is an experimental research model for fast text generation, with output speeds approximately five times faster than Google's previous fastest models, currently available for developer preview through a waitlist.
SynthID Detector is a portal for checking whether images, audio, video, or text were generated by Google's AI tools, currently being rolled out to early testers through a waitlist, with broader access planned for the future.
AlphaEvolve: A Gemini-Powered Coding Agent for Designing Advanced Algorithms#
AlphaEvolve, an evolutionary coding agent driven by the Gemini model, is specifically designed for the discovery and optimization of general algorithms. AlphaEvolve combines the capabilities of two large language models (LLMs), Gemini Flash and Gemini Pro, with the former focusing on breadth exploration and the latter providing depth suggestions, jointly proposing computer program code to achieve algorithmic solutions. By validating, running, and scoring these programs through automated evaluators, AlphaEvolve excels in quantifiable fields such as mathematics and computer science.
AlphaEvolve plays a significant role in Google's computing ecosystem, including data center scheduling, hardware design, and AI model training. For example, it discovered an efficient heuristic algorithm for Google's Borg system, recovering an average of 0.7% of Google's global computing resources, significantly improving data center efficiency. In hardware design, AlphaEvolve proposed optimization suggestions for Google's tensor processing units (TPUs), enhancing the efficiency of matrix multiplication operations. Additionally, it achieved up to a 32.5% acceleration for the FlashAttention core in Transformer models by optimizing GPU instructions.
In the field of mathematics and algorithm discovery, AlphaEvolve has also made breakthrough progress. It proposed a novel gradient optimization process for matrix multiplication, discovering various new algorithms. For instance, it found an algorithm that multiplies 4×4 complex matrices with only 48 scalar multiplications, outperforming the previously considered best Strassen algorithm. Furthermore, AlphaEvolve tested over 50 open problems in mathematical analysis, geometry, combinatorics, and number theory, rediscovering known optimal solutions in about 75% of cases, while improving known best solutions in 20% of cases, such as establishing new lower bounds for the "kissing number problem" in 11-dimensional space.
#Google #AI #Gemini #Agents
AlphaEvolve: A Gemini-powered coding agent for designing advanced algorithms
SMS 2FA is Not Only Insecure but Also Unfriendly to Mountain Residents#
stillgreenmoss describes the issues faced by an elderly woman living in the western North Carolina mountains due to SMS two-factor authentication (SMS 2FA). This woman lives in the mountains, and despite being only a 20-minute drive from town, her home cannot receive stable mobile signals due to the terrain. She uses internet service and a mobile plan provided by Spectrum, but due to poor signal coverage in the mountains, she cannot receive SMS verification codes for logging into accounts, preventing access to important services such as email, bank accounts, and healthcare.
Although she enabled the Wi-Fi calling feature on her phone, she found that SMS verification codes from five-digit short codes still could not be received via Wi-Fi. stillgreenmoss further investigated and found that some landline services provided by certain internet service providers (ISPs) can receive SMS and read them out via computer voice, but Spectrum does not offer such services. To be able to use these services normally, she needed to switch all accounts relying on SMS 2FA to time-based one-time password (TOTP) authentication, but this required her to log into accounts first to change the settings. Therefore, she had to list all the websites she could not access due to SMS 2FA and arrange to meet friends to go to town, where she could change these accounts to TOTP authentication with their help. However, some websites do not support TOTP, and she also needed to contact these companies to request the disabling of SMS 2FA for her accounts, but found it very difficult to reach them.
stillgreenmoss points out that other solutions include transferring her phone number to a VoIP provider that supports Wi-Fi reception of short code SMS, or spending hundreds of dollars to install a mobile signal booster outside her home, or even considering moving, all of which seem very unreasonable. Additionally, while TOTP is an alternative, it requires downloading a dedicated application, and users face many high-risk choices and complex technical instructions when selecting an app.
Despite SMS 2FA performing well in user experience and being technically secure enough, its applicability in mountainous areas is extremely poor. It is estimated that there are 1.1 million people in the western North Carolina mountains, 25 million in the entire Appalachian region, and more living in the western mountains and Pacific coastal mountains, all facing similar issues of poor mobile signal coverage. stillgreenmoss questions that despite these areas having internet access, the F-grade mobile signal coverage makes SMS 2FA nearly unusable for these users, highlighting the limitations of SMS 2FA in specific geographical environments.
#2FA #Security
SMS 2FA is not just insecure, it's also hostile to mountain people — stillgreenmoss
PDF to Text, a Challenging Problem#
Marginalia explores the complexity of extracting text information from PDF files and methods for optimizing text extraction for search engines. The team points out that PDF files are essentially a graphic format rather than a text format, with their content mapped to coordinates on paper, where characters may be rotated, overlapped, and out of order, lacking semantic information, making text extraction highly challenging. Nevertheless, users can still use the search function in PDF viewers, which is an impressive achievement in itself.
Search engines prefer to receive clean HTML format input, and the best current method for PDF to text conversion may be based on visual machine learning models, but this approach is difficult to process hundreds of GB of PDF files on a single server without a GPU. Therefore, the team chose to start with the PDFTextStripper class from Apache PDFBox, which can extract text from PDFs but has many limitations, such as not being able to recognize titles and other semantic information that are crucial for search engines.
To make PDF to text extraction more suitable for search engine needs, the team made several improvements. In recognizing titles, a simple method is to look for semi-bold or bolder text lines, but not all titles use bold fonts; many rely on font size to distinguish. Due to significant font size differences across different documents, it is impossible to find a global breakpoint to distinguish titles from body text; instead, font size statistics need to be built for each page. By analyzing the font size distribution on pages, it can be found that each page usually has a dominant font size, which is the font size of the body text. When extracting titles, using 20% of the median font size on the page as a factor can reliably identify titles, although there are some exceptions.
Additionally, titles may sometimes be split into multiple lines, and the team attempted to merge consecutive title lines into one, but this decision-making is complex. For example, some titles may be right-aligned, or other bold text such as author names may immediately follow the title, making merging titles more challenging. Nevertheless, merging consecutive title lines with the same font size and weight usually yields good results, but some undesirable outcomes may also occur.
In recognizing paragraphs, PDFTextStripper performs well by analyzing line spacing and indentation to determine when to segment paragraphs, but its line spacing logic still has room for improvement. The tool uses fixed line spacing breakpoints, not considering the line spacing differences in different documents, especially in academic drafts and preprints where 1.5 to 2 times line spacing is common. If the line spacing value is too large, it may interfere with title recognition, causing some titles to be misclassified as body paragraphs. To address this issue, the team again adopted a statistical method similar to font size. By analyzing the line spacing distribution of page text, it can be found that the median line spacing is precisely the line spacing used for body text, allowing for the addition of a factor to derive a heuristic method for paragraph separation that can adapt to any line spacing.
Extracting text from PDFs will never be perfect, as the format is not designed for text extraction, and there are trade-offs when choosing a "good enough" solution. Search engines primarily focus on relevance signals, such as titles; if they can recognize summaries and roughly understand the structure of the remaining text, it can be considered a relatively elegant solution.
#PDF #Practice
PDF to Text, a challenging problem
GitHub Copilot Coding Assistant Public Preview#
The GitHub Copilot coding assistant officially entered public preview on May 19, 2025, bringing developers a new programming experience. Developers can assign questions to Copilot just like they would to other developers, and it will run in the background, utilizing the cloud development environment provided by GitHub Actions to explore code repositories, make modifications, and submit code after testing and code standard verification. Once the task is completed, Copilot will notify developers for code review, and developers can request modifications from Copilot in pull requests or continue development in local branches, with Copilot assisting throughout.
Copilot excels at handling low to medium complexity tasks, such as adding features to well-tested codebases, fixing bugs, expanding tests, refactoring code, and improving documentation, even managing multiple issues simultaneously. This feature is currently available to Copilot Pro+ and Copilot Enterprise subscribers, and using it will consume GitHub Actions minutes and Copilot premium request counts, starting from the benefits included in the plan. Starting June 4, 2025, each model request from Copilot coding assistant will use one premium request, which is a preview feature and may change in the future.
#Github #Copilot #AI
GitHub Copilot coding agent in public preview - GitHub Changelog
Komiko#
Komiko is a one-stop AI platform focused on providing creation support for comics, illustrations, and anime works. Developed by the Caffelabs team, the platform integrates various powerful AI tools aimed at helping artists and creators quickly and efficiently turn their creative ideas into reality.
Komiko's core features include character design, comic creation, illustration generation, and animation production. In character design, the platform offers a rich character library, allowing users to create and use their original characters, ensuring consistency in appearance across different scenes. For comic creation, Komiko provides an AI-driven canvas where users can freely arrange comic panels, add dialogue bubbles and effects, enhancing storytelling expressiveness. The illustration generation feature supports various operations such as generating images from text, auto-coloring line art, image upscaling, background removal, and re-lighting, significantly saving time and effort in manual creation. In animation production, Komiko leverages industry-leading AI models, such as Veo, Kling, Hailuo, and Pixverse, to transform keyframes into smooth, high-quality animations and accelerate professional animation production processes through frame interpolation and video upscaling tools.
#AI #Anime #Illustration
Komiko – AI Anime Generator | Create Comics, Manga and Anime with AI
git-bug#
git-bug is a distributed, offline-first defect tracking tool that embeds issues, comments, and more into Git repositories, storing them as objects rather than files. This design allows users to synchronize issue tracking data through Git's push and pull operations. The core advantage of git-bug lies in its deep integration with Git, enabling users to create, edit, and manage issues while offline, and then seamlessly sync to remote repositories. Additionally, it supports synchronization with platforms like GitHub and GitLab through third-party bridges, allowing users to interact with git-bug via command-line interface (CLI), terminal user interface (TUI), or web interface, flexibly choosing their preferred usage method.
#Tools #Git
OpenAI Team Releases Codex#
The OpenAI team has released Codex, a cloud-based software engineering agent tool capable of processing multiple tasks in parallel, powered by codex-1. Codex is optimized for software engineering, trained through reinforcement learning in various real coding task environments, capable of generating code that aligns with human style and code review preferences, accurately following instructions, and continuously running tests until passing. Currently, Codex is available to ChatGPT Pro, Enterprise, and Team users, with plans to support Plus and Edu users in the future.
Users can access Codex through the sidebar of ChatGPT, assigning new coding tasks to it, such as writing functional code, answering questions related to codebases, fixing bugs, and proposing pull requests for review. Each task runs in an isolated environment preloaded with the user's codebase. Codex can read and edit files, running various commands including testing frameworks, code checkers, and type checkers. Task completion times typically range from 1 to 30 minutes, depending on task complexity, and users can monitor Codex's progress in real-time.
The security design of Codex is crucial. It is released in a research preview format, following OpenAI's iterative deployment strategy. During design, the team prioritized safety and transparency, allowing users to verify its output. Users can check Codex's work through citations, terminal logs, and test results. When Codex encounters uncertainty or test failures, it clearly informs users of these issues to enable informed decision-making. However, users still need to manually review and verify all code generated by the agent before integration and execution.
In training codex-1, the team's main goal was to ensure its output aligns with human coding preferences and standards. Compared to OpenAI o3, codex-1 can generate cleaner patches more consistently, which are ready for immediate human review and can seamlessly integrate into standard workflows.
The launch of Codex brings new possibilities to software development. The OpenAI team has explored Codex's performance across different codebases, development processes, and teams through internal testing and collaboration with external partners. Codex can help developers realize ambitious ideas faster, accelerating feature development, debugging issues, writing and executing tests, and refactoring large codebases. It also allows engineers to run complex tasks in the background, keeping them focused and speeding up iteration.
Additionally, the OpenAI team has released an updated version of Codex CLI, a lightweight open-source coding agent that runs in the terminal. It brings the powerful capabilities of models like o3 and o4-mini into local workflows, enabling developers to complete tasks faster. The new version of codex-1 is specifically designed for Codex CLI, supporting faster workflows while maintaining the same advantages in instruction adherence and style.
Codex is currently in the research preview stage and has some limitations, such as lacking image input capabilities required for front-end work and not being able to perform course corrections while working. However, as model capabilities improve, Codex is expected to handle more complex tasks, and interactions with developers will increasingly resemble asynchronous collaboration with colleagues.
In the future, the OpenAI team plans to introduce more interactive and flexible agent workflows. Developers will be able to provide guidance during task execution, collaborate with agents to formulate implementation strategies, and receive proactive progress updates. The team also plans to integrate Codex more deeply with tools developers use daily, such as assigning tasks from Codex CLI, ChatGPT Desktop, or issue trackers and CI systems.
#OpenAI #Codex #AI
Coinbase Claims Hackers Bribed Employees to Steal Customer Data and Demand $20 Million Ransom#
According to CNBC, cryptocurrency exchange platform Coinbase has suffered a serious cyberattack. Attackers bribed overseas customer service personnel to obtain some customer data and demanded a $20 million ransom from Coinbase. Coinbase received a ransom email on May 11, claiming that the attackers had obtained some Coinbase customer account information and other internal documents, including materials related to customer service and account management systems.
Coinbase disclosed this incident in a filing with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission, stating that the potential costs of remediation related to this data breach could reach up to $400 million. Nevertheless, Coinbase emphasized that the breach did not involve users' passwords, private keys, or funds; the affected data primarily included sensitive information such as customer names, addresses, phone numbers, emails, partial bank account numbers, government identification images, and account balances. Coinbase mentioned in its blog that the attackers recruited a group of overseas customer service personnel, exploiting their access to the customer support system to steal some customer account data for social engineering attacks.
After discovering this security vulnerability, Coinbase immediately fired the involved employees and warned potentially affected customers while enhancing fraud monitoring protections. Additionally, Coinbase stated that it would not pay the ransom but instead established a $20 million reward fund for information leading to the arrest and conviction of the attackers.
Coinbase is the largest cryptocurrency exchange platform in the U.S., recently announcing its acquisition of the cryptocurrency derivatives exchange Deribit and is set to enter the S&P 500 index. Despite facing this security challenge, Coinbase's CEO Brian Armstrong stated that the company aims to become a leading financial services application globally within the next five to ten years.
#Crypto #Security
Coinbase says hackers bribed staff to steal customer data and are demanding $20 million ransom
Material 3 Expressive: A Better, Simpler, and More Emotional User Experience#
The Google Design team details the development process and core concepts of the Material 3 Expressive design system. Material 3 Expressive is the most thoroughly researched update to Google's design system to date, with its design philosophy stemming from the exploration of emotionally-driven user experiences.
In 2022, Google's research interns sparked discussions within the team about the homogenization of application interfaces and the lack of emotional expression while studying user emotional feedback on Material Design in Google applications. Subsequently, the team conducted three years of research and design iterations, carrying out 46 independent studies involving over 18,000 global participants, testing hundreds of design proposals, ultimately forming the Material 3 Expressive design principles. These principles are based on solid user research and adhere to long-standing usability best practices, aimed at helping designers create products that are both aesthetically pleasing and highly usable.
The core of Material 3 Expressive lies in emotional design, which stimulates user emotions through design elements such as color, shape, size, motion, and layout, while helping users achieve their goals. Research shows that emotional design is strongly preferred by users of all ages, especially among the 18 to 24 age group, where preference rates reach 87%. These users believe that emotional design excels in "visual appeal" and "willingness to use."
During the research process, the team employed various methods, including eye-tracking, surveys and focus groups, experiments, and usability testing. For instance, when testing progress indicators, the team evaluated which designs made waiting times feel shorter while still aligning with high-end mobile design styles; when studying button sizes, the team sought to balance increasing click speed with avoiding interference between interface elements. Additionally, the team conducted multiple studies on the new floating toolbar, optimizing its modern, clean, vibrant, and user-friendly design.
Emotional design not only enhances the visual appeal of products but also significantly boosts the modernity and relevance of brands. Research indicates that products designed with Material 3 Expressive principles improved "subcultural perception" by 32%, "modernity" by 34%, and "rebelliousness" by 30%. These data suggest that emotional design can make brands appear more cutting-edge, innovative, and daring to break from tradition.
More importantly, emotional design plays a key role in enhancing user experience. Through eye-tracking experiments, participants using applications designed with Material 3 Expressive were able to notice key UI elements four times faster than with traditional designs. For example, in an email application, the new "send" button is larger, positioned lower, and uses an accent color, allowing users to find and click it more quickly. Furthermore, emotional design has narrowed the visual localization time gap between different age groups, enabling users over 45 to find key interactive elements as quickly as younger users.
Despite the many benefits of emotional design, it is not suitable for all scenarios. For example, in applications that need to adhere to traditional UI patterns, excessive emotional design may lead to decreased usability. Therefore, designers need to consider context when applying emotional design, respecting existing design patterns and standards.
To help designers better apply Material 3 Expressive design, the Google Design team offers a series of suggestions: first, encourage designers to experiment with new design options, such as the updated Figma Material 3 design toolkit; second, suggest that designers flexibly apply emotional design strategies in conjunction with users' core journeys; third, emphasize starting from user needs, prioritizing functionality and adherence to accessibility standards; and finally, recommend finding a balance between novelty and familiarity, playfulness and professionalism through continuous research and iteration.
#Google #Design #Material